Documentation
- Speed Test
- Speed Test
- Prioritize Connections
- Prioritize Connections
- DiffServ
- DiffServ
- Merge with games
- Merge with games
- Accelerate your online games
- Accelerate your online games
- Improve Shared Connections
- Improve Shared Connections
- Prioritarize a Port
- Prioritarize a Port
- Prioritarize a Program
- Prioritarize a Program
- Backup/Restore
- Backup/Restore
- Generic Speed Guide
- Generic Speed Guide
- Create Dump
- Create Dump
- Surf the Web Faster
- Surf the Web Faster
- Create a Wifi Access Point
- Create a Wifi Access Point
- Create Skin
- Create Skin
- Speed Test
- Speed Test
- Prioritize Connections
- Prioritize Connections
- DiffServ
- DiffServ
- Merge with games
- Merge with games
- Accelerate your online games
- Accelerate your online games
- Improve Shared Connections
- Improve Shared Connections
- Prioritarize a Port
- Prioritarize a Port
- Prioritarize a Program
- Prioritarize a Program
- Backup/Restore
- Backup/Restore
- Generic Speed Guide
- Generic Speed Guide
- Create Dump
- Create Dump
- Surf the Web Faster
- Surf the Web Faster
- Create a Wifi Access Point
- Create a Wifi Access Point
- Create Skin
- Create Skin
- Status Window
- Status Window
- Status Window on phone/tablet
- Status Window on phone/tablet
- Wi-Fi access point Online Budgets
- Wi-Fi access point Online Budgets
- Usage Graph
- Usage Graph
- Logitech keyboard support
- Logitech keyboard support
- Keyboard LEDs
- Keyboard LEDs
- The cFosSpeed Configuration-dialog
- The cFosSpeed Configuration-dialog
- Save Settings
- Save Settings
- Additional languages for cFosSpeed
- Additional languages for cFosSpeed
- Technical references for experts (English only)
- Technical references for experts (English only)
- SPD.EXE Commands
- SPD.EXE Commands
- Status Window
- Status Window
- Status Window on phone/tablet
- Status Window on phone/tablet
- Wi-Fi access point Online Budgets
- Wi-Fi access point Online Budgets
- Usage Graph
- Usage Graph
- Logitech keyboard support
- Logitech keyboard support
- Keyboard LEDs
- Keyboard LEDs
- The cFosSpeed Configuration-dialog
- The cFosSpeed Configuration-dialog
- Save Settings
- Save Settings
- Additional languages for cFosSpeed
- Additional languages for cFosSpeed
- Technical references for experts (English only)
- Technical references for experts (English only)
- SPD.EXE Commands
- SPD.EXE Commands
- Game Analyzer
- Game Analyzer
- RWIN Expansion
- RWIN Expansion
- Traffic Shaping for Filesharing (P2P)
- Traffic Shaping for Filesharing (P2P)
- Suggestions for gamers
- Suggestions for gamers
- Prioritizing programs
- Prioritizing programs
- Prioritizing ports
- Prioritizing ports
- What alternative Internet tuning methods are there?
- What alternative Internet tuning methods are there?
- Task Offloading with cFosSpeed
- Task Offloading with cFosSpeed
- cFos Speed Guide
- cFos Speed Guide
- Game Analyzer
- Game Analyzer
- RWIN Expansion
- RWIN Expansion
- Traffic Shaping for Filesharing (P2P)
- Traffic Shaping for Filesharing (P2P)
- Suggestions for gamers
- Suggestions for gamers
- Prioritizing programs
- Prioritizing programs
- Prioritizing ports
- Prioritizing ports
- What alternative Internet tuning methods are there?
- What alternative Internet tuning methods are there?
- Task Offloading with cFosSpeed
- Task Offloading with cFosSpeed
- cFos Speed Guide
- cFos Speed Guide
- What is Traffic Shaping?
- What is Traffic Shaping?
- How does Traffic Shaping work?
- How does Traffic Shaping work?
- L7 Protocol Analysis
- L7 Protocol Analysis
- Prioritization of Programs
- Prioritization of Programs
- Class Delay Management
- Class Delay Management
- RTP/VoIP Detection
- RTP/VoIP Detection
- Individual rules with filter language
- Individual rules with filter language
- Traffic Shaping options / Multi-User version
- Traffic Shaping options / Multi-User version
- DiffServ / DSCP tagging
- DiffServ / DSCP tagging
- cFosSpeed with torrents
- cFosSpeed with torrents
- What is Traffic Shaping?
- What is Traffic Shaping?
- How does Traffic Shaping work?
- How does Traffic Shaping work?
- L7 Protocol Analysis
- L7 Protocol Analysis
- Prioritization of Programs
- Prioritization of Programs
- Class Delay Management
- Class Delay Management
- RTP/VoIP Detection
- RTP/VoIP Detection
- Individual rules with filter language
- Individual rules with filter language
- Traffic Shaping options / Multi-User version
- Traffic Shaping options / Multi-User version
- DiffServ / DSCP tagging
- DiffServ / DSCP tagging
- cFosSpeed with torrents
- cFosSpeed with torrents
Program
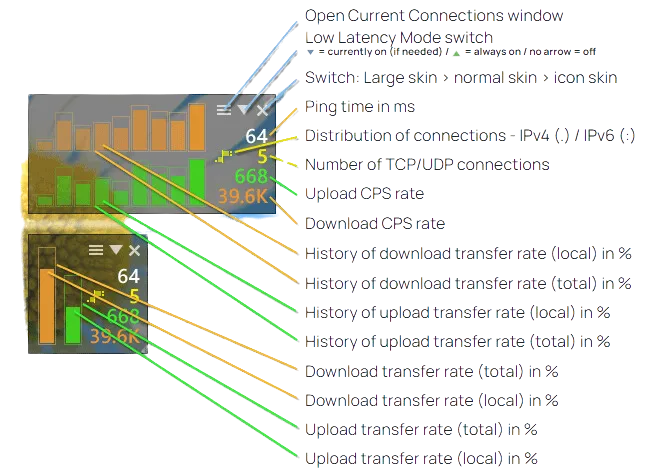
All you need to know about the cFosSpeed Status Windows and Skins
The cFosSpeed Status Windows display important statistics about your current Internet connection. You should choose the skin most useful to you, e.g. the icon skins which integrate into the task bar or the Traffic Analysis skin with real-time statistics about your current different traffic types. Please vote on the different skins. This will help us when designing the next skin window.
Metro Skin
Deactivating the cFosSpeed status window
You can deactivate the cFosSpeed status window by right-clicking on it, selecting Window Settings and then deactivating “Auto-show/Auto-hide”.
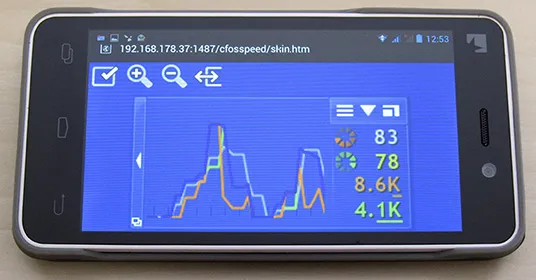
Status Window on phone/tablet
Beginning with v9.05 build 2090 cFosSpeed has a build-in web server, so you can display the status window on your phone or tablet, in addition to your desktop. This is especially helpful for fullscreen applications like games or videos. Here is how to configure it:
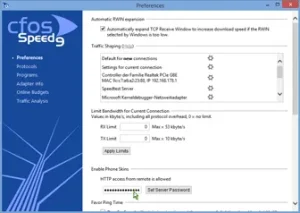
- Start “Options/Settings” from the cFosSpeed context menu and set a server password in the “Preferences/Enable Phone Skins” dialog. The web server will need authorization if you access it from another machine than your local computer.
- Open the context menu and select the first option (cFosSpeed vX.XX…) to display your local IP addresses.
- Open the browser on your phone or tablet and enter the following address: http://[Your IP address]:1487/cfosspeed/skin.htm. [Your IP address] is usually the first listed address from step 2, but you can try all others if the first doesn’t work.
- Now fill the authentification dialog with “cfosspeed” as username and the server password you configured under “Preferences/Enable Phone Skins” as password.
Note: You can also view and prioritize your current connections from your phone or tablet. Simply open http://[Your IP address]:1487/cfosspeed/console.htm in your browser. This dialog works as if started from the cFosSpeed status window or context menu.
Note: You need Windows 7 or higher to use the built-in web server.
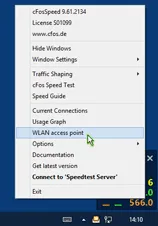
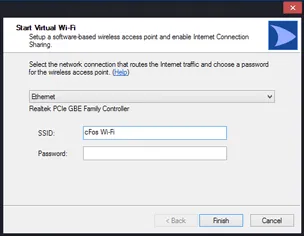
Wi-Fi access point
Enable>cFos Traffic Shaping for smartphones, tablets and other mobile devices.
Windows 7, 8 and 8.1 allow you to use your Wi-Fi adapter as an ad hoc Wi-Fi access point. So other devices can connect to your PC (instead of directly to the Wi-Fi router) and therefore can benefit from cFosSpeed Traffic Shaping.
cFosSpeed now has a context menu option to start and configure (or stop) the Wi-Fi access point easily.
If your PC is connected to the router via Wi-Fi, you can share the same adapter for the ad hoc Wi-Fi access point. Or you can use the Wi-Fi adapter exclusively for the Wi-Fi access point if your PC is connected to the router via network cable. In this case the Wi-Fi bandwidth is fully available for your mobile devices, like smartphone or tablet.
When you have cFosSpeed installed on this PC, the Wi-Fi data is routed through cFosSpeed and, via its Layer-7 protocol detection, cFosSpeed can prioritize the traffic. If you frequently use smartphones and tablets for VoIP or streaming traffic, like music or movies, we recommend to add a Wi-Fi adapter to your PC and route the traffic of your mobile devices through this PC and cFosSpeed.
Manually set up a Wi-Fi access point (Windows 7 and above)
Open the command shell as Administrator:
C:\Program Files\cFosSpeed>netsh wlan set hostednetwork mode=allow
Open the command shell as Administrator:
C:\Program Files\cFosSpeed>netsh wlan set hostednetwork ssid=”cFos Wi-Fi” key=”your_password” keyUsage=persistent
Check with:
C:\Program Files\cFosSpeed>netsh wlan show hostednetwork
Start “Microsoft Virtual WiFi Miniport Adapter”.
C:\Program Files\cFosSpeed>netsh wlan start hostednetwork
Check with:
C:\Program Files\cFosSpeed>netsh wlan show hostednetwork
In the list of network connections the red cross next to “Microsoft Virtual WiFi Miniport Adapter” should have been disappeared.
Right click in the list of network connections on the active Internet connection and select “Properties” from the menu. Click the “Sharing” tab, and then select the “Allow other network users to connect through this computer’s Internet connection” check box.
Under “Home networking connection” select the connection that shows the “Microsoft Virtual WiFi Miniport Adapter” in the list of network connections.
Confirm with “OK”.
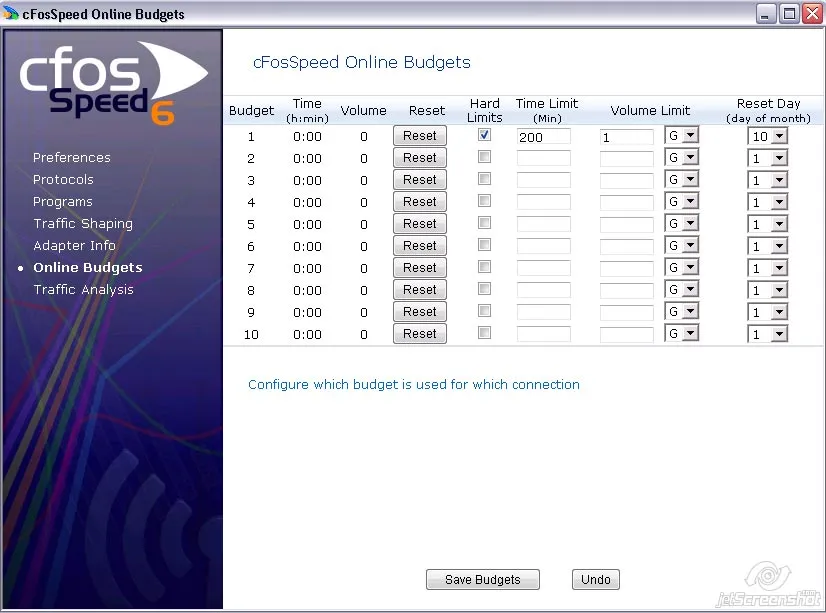
Online Budgets
Since cFosSpeed version 3.10 you can individually config and administrate up to 10 data and time-budgets.
You can access the configuration dialog via the cFosSpeed Menu:
·>Options ·>Online Budgets
For each Budget you can set a time, a data volume budget or both. In addition you have the possibility to set hard limits which allows you to have full control. You can also choose a reset day for the budgets or reset them manually.
To assign a budget to a certain connection use the cFosSpeed connection dialog at
·>Options ·>Traffic Shaping ·>Options
The budgets are visualised by usage graphs.
Example
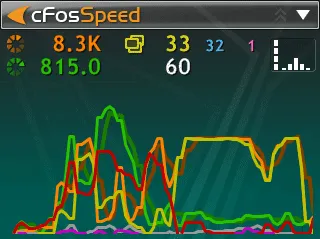
Usage Graph
cFosSpeed can show a Usage Graph for online budgets, protocols or programs. You also can choose if the display refers to the current month, to the past month, ot the past 3 month or to the past 12 month. Further you can choose the following ways of display:
- rx – display: amount of download data
- tx – display: amount of upload data
- rx+tx – display: sum of amount of upload and download data
- sum – display: total amount of data is shown in a continuous sum.
Online Budgets
Steps to set a Usage Graph for a online budget:
- At ‘Settings/Traffic Shaping’ you can assign a budget X to your connection.
- Now open the Usage Graph window by ‘Usage Graph’.
- Select your display colour and choose ‘Online budgets’ from the list.
- Into the sublist choose the budget number X.
Protocols/Programs
Steps to set a Usage Graph for a protocol or a program:
- Open the Usage Graph window by ‘Usage Graph’.
- Select your display colour and choose ‘Protocols’ or ‘Programs’ from the list.
- Into the sublist choose the protocol or the program.
Example
Logitech keyboard support
cFosSpeed supports the Logitech gamer keyboards G19, G15, G13, G510 and compatible models. In order to use the display of such a gaming keyboard, the Logitech Gaming Software V7.00 or higher must be running. Then you can navigate to the cFosSpeed window settings menu and activate Logitech display support. Now the cFosSpeed status window is displayed on the keyboards display instead of the Windows desktop.
We suggest you use the following skins.
Logitech skins on YouTube
Use keyboard LEDs to display Traffic Shaping information
cFosSpeed can use the Num Lock and Scroll Lock LEDs to display information about the current Internet traffic. This is especially useful for gamers and users of fullscreen application, who can’t see the cFosSpeed status window. By using the keyboard LEDs the most important traffic statistics are indicated:
- ping:
- off, fair = slow blink, bad = fast blink
warns you if the ping time is too high - pcnt:
- fast blinking as packets are counted
informs you about any traffic to/from the internet - ts_effect:
- fast blink when a TX packet is prioritized
one of the ways to indicate the effects of Traffic Shaping - speed:
- maximum of total_rx_speed and total_tx_speed, 0-32%: off, 33-65%: slow blink, 66-98%: fast blink 99-100%: on
informs you, when you or another user / application uses (too) much bandwidth - ccnt:
- fast blink whenever the sum of TCP and UDP connections changes
you stay informed if some new connection is established - variance:
- 0-15ms: off, 16-127ms: slow blink, 128-511ms: fast blink, 512ms or more: on
informs you if line conditions (e.g. mobile connections) cause high ping variance
You can select the Num Lock and Scroll Lock LEDs to display any of the above values.
Hint: The actual script for controlling the keyboard LEDs is a javaScript, called led.js. So if you like to display other variables or use a completely different LED blinking scheme, feel free to change it to your needs.
The cFosSpeed Configuration-dialog
To configure settings for your connections please open the regarding window via Settings/Traffic Shaping. Here you will find an overview over all connections. The table ‘Dial-up Connections’ shows all Windows Broadband and Dial-Up connections. The table ‘Network Components’ shows all network components and routers. For each connection you can configure whether to achtivate (Yes) or deactivate (No)Traffic Shaping. As a third option you can opt to always be asked first(Ask) or use the default mode(default) with the routers.
Please click on Settings/Preferences to open the extended settings window. For this connection you can choose a budget, set the medium and the Traffic Shaping modus.
Example
Save Settings
cFosSpeed stores its settings in the following files:
C:\ProgramData\cFos\cFosSpeed
- data.ini
- global.ini
- settings.ini
- user.ini
C:\Users\[username]\AppData\Local\cFos\cFosSpeed
- user_data.ini
You can backup all 5 files.
In addition, if you want to keep the online budget log files you should backup the subdirectory logs: C:\ProgramData\cFos\cFosSpeed\logs.
To restore the settings just restore global.ini, user.ini, data.ini. Settings.ini is overwritten by new installations. Therefore if you also made changes in settings.ini, you need to apply these again in the new settings.ini. Otherwise use the settings.ini from the most recent installed version.
Additional languages for cFosSpeed
Writing a cFosSpeed multi-language file for your own language
Installation Instructions
- Download the language files and unzip them. You should get two text files.
- Put these text files in the same directory as the file cfosspeed.exe that you’ve downloaded from our web site.
- Execute cfosspeed.exe and select your language in the welcome dialog.
- Continue the installation.
- After a successful installation you can also change the language from the pop-up menu of the cFosSpeed taskbar icon.
Language Files
Disclaimer:
As a service to you, we have made the following cFos/cFosSpeed localizations available for free download. Since these free expansions have been created by customers for customers, cFos Software GmbH does neither assume liability nor provide technical support for any of them.
For any questions concerning a specific localization, please do contact the author directly. However, should you come across any significant translation errors, omissions or other irregularities (intentional or otherwise), please let us know briefly so we can check up on it.
Technical references for experts (English only)
This reference is divided into several sub-pages:
- Traffic classes
- Filter expressions – Rules you can use to filter packets to traffic classes
- IP lists – Load large lists of IP addresses in Emule or Protowall/Peerguardian format
- Net_talk – Multiple cFosSpeed’s communicating in your LAN
- Miscellaneous information
- DATA.INI
That’s it.
Have fun shaping your traffic!
Detailed description of spd commands (with examples)
spd command – overview
To use spd commands you can enter them on the cFosSpeed console, which can be open by
START/Programs/cFosSpeed/cFosSpeed Console
If you enter the command spd help you get the following list of commands:
- set port specific variable (set <v> /? for help)
- module <name> on/off
- switch module <name> on or off
- perf on/off
- switch statistics display on/off
- close
- close LAN port
- ping
- send a echo request.
- sethops
- set the TTL for outgoing test pings.
- speed
- show current shaper settings.
- medium
- set connection characteristics (medium /? for help)
- tsclear
- clear the traffic shaping settings for this connection.
- class
add a new traffic class or change settings on an existing one.
- -speed <x>
- sets the speed to <x>. use ‘inf’ to specify infinite speed.
- -prio <x>
- sets the priority to <x>
- -dscp <x>
- set DSCP value of packets to <x>. use ‘none’ to not set.
- -clear
- clears the stats.
- cstat
- print all classes with stats. accepts a wildcard like ‘*’ or ‘f*’. -clear clear stats afterwards.
- filter
show/add/modify filters. -print prints filters after the operation.
- <no option>
- show all filters
- -A <f>
- append filter <f> at the end.
- -D <num>
- delete filter at position <num>
- -I <num> <f>
- insert filter <f> at position <num>
- -R <num> <f>
- replace filter at position <num> with filter <f>
- -M <old> <new>
- move filter from position <old> to <new>
- reload
reload settings from ini file.
- -filter
- reload filters
- save
save filter/class settings to ini file.
- -class
- save classes
- -filter
- save classes or filters.
- addkey <section> <key>
- add <key> to <section> in settings.ini
- delkey <section> <key>
- delete <key> from <section> in settings.ini
- showsect <section>
- show section <section> in settings.ini
- fwstat
- show firewall statistics (-clear to clear after display)
- fstat
- show all filter statistics (-clear to clear after display)
- netstat
- print global network protocol statistics
- pingstat
- print ping statistics (-clear clears stats after printing)
- cons
- list of tcp connections (-cps for cps, -vol for volume)
- budget
- show active budget’s settings and stats
- burst
- start a burst of data to check line speed
- ports
- list all ports
- pcnt
- show packet counters
- ver
- print cFosSpeed version info
- dump
- on/off/in/out/net/app/ign/ip/ipr dump of network packets
- gset
- set global variable (-save to save it to ini file)
- tvstat
- print tcpview statistics
- prognames
- print known program names
- reset_budget
- reset online budget
Description of spd commands (with examples)
spd set
With spd command set different cFosSpeed values can be set manually. You can get an overview of all values by simply entering spd set.
If you want to change a value manually,the following command structure applies : spd set = ‘value’.
To get detailed instruction, type set /?
Example: Output from spd set
C:\Programme\cFosSpeed>spd set avg_time = 4000 budget = 0 burst_cnt = 3 curr_max_rx = 791599 curr_max_tx = 1055763 delay_auto = 1 fixed = 0 high_diff_cnt = 1683 inhibit_bridged = 0 low_diff_cnt = 1360 maxdelay = 24102267 maxiplen = 1492 maxrx = 6030441 maxtxacked = 1433436 maxtxraw = 1445060 medium = adaptive (0) method = adaptive (8) mindelay = 8186 net_talk = 1 net_talk_bcast = 0.0.0.0 perf = 0 ping_cnt = 113804 pong_cnt = 103173 record_packet_sizes_rx = 0 reg_id = 3 rx_delay = 20000 rx_limit = inf rx_width = 1497 tcp_cons = 42836 time_used = 885530 tx_bounce_cnt = 5 tx_delay = 10000 tx_limit = inf tx_width = 1000 txspeed = 1517313 udp_cons = 42679 vari_fixed = 0 variance = 5121 vollso = 9699544186 (9250M) volrsc = 0 (0) volrx = 19347327844 (18.01G) voltxacked = 10165906693 (9694M) voltxraw = 11648109237 (10.84G) wperf = 0
Example: Changing the fixed value to 1
C:\Programme\cFosSpeed>spd set fixed=1 fixed = 1
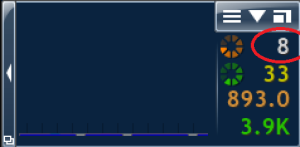
spd ping
The spd command ping sends a single measuring ping. The current value of the ping time then flashes briefly in the numerical cFosSpeed status window. In the example this is the value 8 ms
Example
C:\Programme\cFosSpeed>spd ping
- set port specific variable (set <v> /? for help)
- module <name> on/off
- switch module <name> on or off
- perf on/off
- switch statistics display on/off
- close
- close LAN port
- ping
- send a echo request.
- sethops
- set the TTL for outgoing test pings.
- speed
- show current shaper settings.
- medium
- set connection characteristics (medium /? for help)
- tsclear
- clear the traffic shaping settings for this connection.
- class
add a new traffic class or change settings on an existing one.
- -speed <x>
- sets the speed to <x>. use ‘inf’ to specify infinite speed.
- -prio <x>
- sets the priority to <x>
- -dscp <x>
- set DSCP value of packets to <x>. use ‘none’ to not set.
- -clear
- clears the stats.
- cstat
- print all classes with stats. accepts a wildcard like ‘*’ or ‘f*’. -clear clear stats afterwards.
- filter
show/add/modify filters. -print prints filters after the operation.
- <no option>
- show all filters
- -A <f>
- append filter <f> at the end.
- -D <num>
- delete filter at position <num>
- -I <num> <f>
- insert filter <f> at position <num>
- -R <num> <f>
- replace filter at position <num> with filter <f>
- -M <old> <new>
- move filter from position <old> to <new>
- reload
reload settings from ini file.
- -filter
- reload filters
- save
save filter/class settings to ini file.
- -class
- save classes
- -filter
- save classes or filters.
- addkey <section> <key>
- add <key> to <section> in settings.ini
- delkey <section> <key>
- delete <key> from <section> in settings.ini
- showsect <section>
- show section <section> in settings.ini
- fwstat
- show firewall statistics (-clear to clear after display)
- fstat
- show all filter statistics (-clear to clear after display)
- netstat
- print global network protocol statistics
- pingstat
- print ping statistics (-clear clears stats after printing)
- cons
- list of tcp connections (-cps for cps, -vol for volume)
- budget
- show active budget’s settings and stats
- burst
- start a burst of data to check line speed
- ports
- list all ports
- pcnt
- show packet counters
- ver
- print cFosSpeed version info
- dump
- on/off/in/out/net/app/ign/ip/ipr dump of network packets
- gset
- set global variable (-save to save it to ini file)
- tvstat
- print tcpview statistics
- prognames
- print known program names
- reset_budget
- reset online budget
Description of spd commands (with examples)
spd set
With spd command set different cFosSpeed values can be set manually. You can get an overview of all values by simply entering spd set.
If you want to change a value manually,the following command structure applies : spd set = ‘value’.
To get detailed instruction, type set /?
Example: Output from spd set
C:\Programme\cFosSpeed>spd set avg_time = 4000 budget = 0 burst_cnt = 3 curr_max_rx = 791599 curr_max_tx = 1055763 delay_auto = 1 fixed = 0 high_diff_cnt = 1683 inhibit_bridged = 0 low_diff_cnt = 1360 maxdelay = 24102267 maxiplen = 1492 maxrx = 6030441 maxtxacked = 1433436 maxtxraw = 1445060 medium = adaptive (0) method = adaptive (8) mindelay = 8186 net_talk = 1 net_talk_bcast = 0.0.0.0 perf = 0 ping_cnt = 113804 pong_cnt = 103173 record_packet_sizes_rx = 0 reg_id = 3 rx_delay = 20000 rx_limit = inf rx_width = 1497 tcp_cons = 42836 time_used = 885530 tx_bounce_cnt = 5 tx_delay = 10000 tx_limit = inf tx_width = 1000 txspeed = 1517313 udp_cons = 42679 vari_fixed = 0 variance = 5121 vollso = 9699544186 (9250M) volrsc = 0 (0) volrx = 19347327844 (18.01G) voltxacked = 10165906693 (9694M) voltxraw = 11648109237 (10.84G) wperf = 0
Example: Changing the fixed value to 1
C:\Programme\cFosSpeed>spd set fixed=1 fixed = 1
spd ping
The spd command ping sends a single measuring ping. The current value of the ping time then flashes briefly in the numerical cFosSpeed status window. In the example this is the value 8 ms
Example
C:\Programme\cFosSpeed>spd ping
spd sethops
With the command sethops you can set the ttl value of the cFosSpeed measure pings. Just set the number i for the value. The output is: “addhops 2+i (ttl i)“, where first you get the variation from the default value (2). Then you get the current and new ttl-value.
Hint: The command only works, if you are online. If you are not you will get the error message: cannot perform command; section name still unknown
Example: set ttl-value to 5
C:\Programs\cFosSpeed>spd sethops 5 add_hops = 3 (ttl 5)
see also:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Time_to_live
spd speed
With the spd command “speed”, you get an overview of various traffic shaping values. The most important are:
- maxrx – maximum download bandwidth in cps
- method – Information about the transmission method used: PPPoE, PPPoA, PPPtP, Cable, etc.
- addhops – here the current ttl value is displayed in brackets.
- pingcnt – total number of pings sent
- pongcnt – total number of ping responses (pongs) received
- txspeed – Upload bandwidth in cps
Example:
C:\Programme\cFosSpeed>spd speed Current shaper settings (v13.00.3000): maxtxraw=1445K maxtxacked=1433K maxrx=6030K avg_time=4000 mindelay=7441 variance=3896 vari_fixed=0 reg_id=3 method=adaptive (8) pinger=udp_km3 voltxraw=10.86G voltxacked=9704M volrx=18.36G time_used=10d 7h maxiplen=1492 rx_limit=inf tx_limit=inf inhibit_bridged=0 ping_cnt=115966 pong_cnt=105300 (90.8%) burst_cnt=3 adapter=WIFI link speed: rx=108.3M tx=43.87M txspeed=1517K fixed=0 tx_bounce_cnt=5 calibrated=100 tx delay=10000-14896 rx delay=20000-25393 delay_auto=1
spd tsclear
The command “spd tsclear” clears the traffic shaping settings for the current connections. The current data in the corresponding section of the data.ini file is deleted. The connection can now be recalibrated.
Example:
C:\Programme\cFosSpeed>spd tsclear traffic shaping settings cleared.
spd dump
With the “dump” command you can write a text file (dump.txt) that records all datapackets.
Example:
C:\Programme\cFosSpeed>spd dump ip dump ip (64) dump data: IP packets. C:\Programme\cFosSpeed>spd dump off dump off (0)
functions:
on : turn on writing of dump file
off : turn off writing of dump file
in : dump only incoming data packets
out : dump only outgoing data packets
net :
app :
ign :
ip : dump IP packets (possibly fragmented)
ipr : dump IP datagrams (after IP reassembly).spd cstat
The “cstat” command provides upload statistics for sent data packets of the individual cFosSpeed traffic shaping classes (highest, higher, high, default, low and lowest). The first line of the command output indicates whether traffic shaping is enabled. The upload bandwidth in cps (txspeed) and the maximum queue overflow value are also specified here.
Example:
C:\Programme\cFosSpeed>spd cstat shaping is currently enabled; txspeed = 19659, max_queue_size = 58,977 class highest -prio 100 sent 2,431 ( 4%) packets 68,068 ( 0%) bytes in queue 0 packets 0 bytes class higher -prio 90 sent 16,777 ( 34%) packets 671,716 ( 3%) bytes in queue 0 packets 0 bytes class high -prio 80 sent 10,489 ( 21%) packets 1,235,682 ( 5%) bytes in queue 0 packets 0 bytes class default sent 14,593 ( 29%) packets 19,897,796 ( 90%) bytes in queue 0 packets 0 bytes class low -prio 0 -speed 25%,-10 sent 4,820 ( 9%) packets 221,720 ( 1%) bytes in queue 0 packets 0 bytes class lowest -prio 0 -speed 25%,-30 sent 0 ( 0%) packets 0 ( 0%) bytes in queue 0 packets 0 bytes class drop dropped 0 packets 0 bytes queue overflow 0 packets 0 bytes
spd ver
The “spd ver” command outputs information about the currently installed version. The version number, build number and installation date including the installation time are displayed. You will also receive information about the operating system and processor used. Finally, the current installation date is stated as well as the installation and info directories of cFosSpeed.
Example:
C:\Programme\cFosSpeed>spd ver This is cFosSpeed (x64) v13.00, build 3000 Copyright (c) 2003-2023 Atlas Tech Solutions SM PC -- https://atlas-cfosspeed.comOS: Windows 10 Home Multiprocessor Free (x64) (16 procs) v10.00.22631, LangId 0409 OS build is ???? (x64) (22621.1.amd64fre.ni_release.220506-1250) CPU: 13th Gen Intel(R) Core(TM) i7-1360P, ID 0b06a2h (06_bah, Raptor Lake (Raptor Lake-P)) Time now: 2024-02-07 15:27:44.987 (UTC+1) Load time: 2024-02-07 15:27:14.748 (UTC+1) CPU speed: 5762 cfops Using performance counter running at 10 MHz Timer resolution is 4 msec (coarsest=15.625) Driver base address is 0xfffff8062d4f0000; timestamp is 65841734 (2023-12-21 10:45:08 UTC) Installation directory is "C:\Program Files\cFosSpeed\" Programdata directory is "C:\ProgramData\cFos\cFosSpeed\" Licensed to (End-user license) [A10000]
spd gset
With the copmmand spd “gset” some of the cFosSpeed variables are listed. They switched on (1), off (0) or set to certain value. To switch a function on and off or set it to a certain value you can use commands with the folowing structure “spd gset <function>=X” (where X is 1, 0 or the value to be set)
If you add “-save” you can save the settings and they will be also set after the next reboot of your system.
Enter “spd gset” and you will get:
C:\Programs\cFosSpeed>spd gset analyze_rtp = 1 auto_burst = 1 avoid_loss = 1 balloon_no_pings = 0 bulk_detect = 1 delay_ndis_completions = 0 dump_arp = 0 dump_ascii = 1 dump_framing = 0 dump_relseq = 0 dump_sessions = 0 dump_tcp_data = 0 dump_udp_data = 1 dump_wshark = 0 expand_rwin = 1 expand_rwin_dest_time = 200 fg_detect = 1 filter_fix = 3 firewall = 0 func_trace = 0 fwlog = 1 global_counters = 0 handle_mss = 0 handle_tsopt = 0 l7_detect = 1 latency = 2 log_sessions = 0 max_dump_size = 16777216 (16 M) max_expand_rwin_time = 300 max_fwlog_size = 4194304 (4 M) max_pinglog_size = 1048576 (1 M) max_queue_time = 1000 max_session_dump_size = 100000 max_session_log_size = 1048576 (1 M) max_trace_size = 16777216 (16 M) mcast_router = 0 net_talk_default = 1 net_talk_port = 889 passthru = 0 patch_dns_ttl = 0 ping_fixed = 0 pinglog = 0 prioritize_ssl = 1 reg_id_default = 3 resend_in_queue = 0 router_info = 1 router_stats = 1 rtp_trace = 0 rx_shape = 1 save_in_session = 1 send_usage_metadata = 1 shape = 1 store_dns_names = 1 strict_rtp_check = 1 tcp_warn = 0 traffic_stat = 1 tx_shape = 1 udp_timeout = 10000 user1 = 0 vari_fixed_default = 0 vari_trace = 0 worker_threads = 0
examples
d:\tools>spd gset firewall=1 firewall = 1
Turn off permanently Traffic Shaping:
C:\Programs\cFosSpeed>spd gset shape=0 -save shape = 0 value saved.
C:\Programs\cFosSpeed>spd gset passthru=1 passthru = 1 C:\Programs\cFosSpeed>spd gset passthru=0 passthru = 0
Possible values:
0 : off
1 : ignore all packets, pass them on to the next driver immediately.
2 : ignore all packets, send them through the cFosSpeed connection
engine, but don't do anything with them.
Disable writing of firewall log file fwlog.txt:
C:\Programme\cFosSpeed>spd gset fwlog 0 -save fwlog = 0 value saved.
prevent cFos / cFosSpeed from saving data.ini, budget and traffic stats every 10 minutes: “spd gset save_in_session 0 -save“
C:\Programme\cFosSpeed>spd gset save_in_session 0 -save save_in_session = 0 value saved.
Specify after how many seconds of inactivity the LAN port (and status window) will be closed automatically: “spd gset port_close_time ‘n’ “
C:\Programme\cFosSpeed>spd gset port_close_time 5 port_close_time = 5
spd reset_budget
With the command spd “reset_budget [n]” you can reset online budget with the number ‘n’ (n=0..9). If ‘n’ is omitted the current budget is reset.